What is NMAP?
Nmap is short for Network Mapper. It is an open-source Linux command-line tool that is used to scan IP addresses and ports in a network and to detect installed applications.
Initial Scans
We have to keep in mind, NMAP is an active tool / scanner. This means whatever you run with nmap can be detected on any network that is being monitored. Keep this in mind. For an initial scan, we will scan a subnet quickly just to see what hosts, if any, respond.
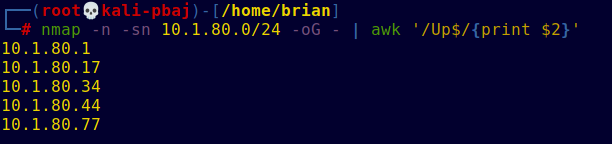
nmap -n -sn 10.x.x.x/24 -oG - | awk '/Up$/{print $2}'
Quick rundown of options and commands:
-nturns off reverse name resolution, since you just want IP addresses. On a local LAN this is probably the slowest step, too, so you get a good speed boost.-snmeans “Don’t do a port scan.” It’s the same as the older, deprecated-sPwith the mnemonic “ping scan.”-oG -sends “grepable” output to stdout, which gets piped toawk./Up$/selects only lines which end with “Up”, representing hosts that are online.{print $2}prints the second whitespace-separated field, which is the IP address.
You can accomplish the same output by also using a combination of awk and cut
We can accomplish the same results above with the following command below using cut.
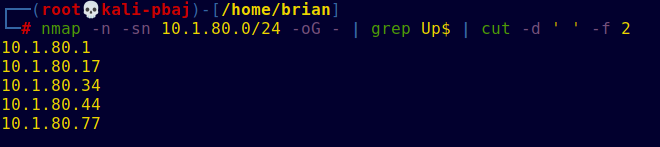
nmap -n -sn 10.1.80.0/24 -oG - | grep Up$ | cut -d ' ' -f 2
Quick rundown of the command:
-nturns off reverse name resolution, since you just want IP addresses. On a local LAN this is probably the slowest step, too, so you get a good speed boost.-snmeans “Don’t do a port scan.” It’s the same as the older, deprecated-sPwith the mnemonic “ping scan.”-oG -sends “grepable” output to stdout, which gets piped tocut.grep Up$selects only lines which end with “Up”, representing hosts that are online.{cut -d ' ' -f 2}prints the second whitespace-separated field, which is the IP address.